Workflow
A workflow is a logical process used to define, manage, and automate interactions between devices, data, and services. Workflow can connect multiple predefined rules or tasks in series to implement rich and flexible functions, such as threshold alarms and schedule switches.
Add Workflow
-
Go to Workflow page, click +Add to add workflows.
-
Select the starting node of this workflow as required, click Create.
| Start Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Timer | Trigger the workflow based on the schedule time or cycle. Example: schedule switch. |
| Trigger | Trigger the workflow by the Trigger widget on the Dashboards. Example: button switch. |
| Entity Listener | Trigger the workflow when any entity data changes. Example: threshold alarm. |
| MQTT Listener | Work as MQTT broker to listen for incoming MQTT messages to trigger a running workflow. |
| HTTP Listener | Work as HTTP server to listen for incoming MQTT messages to trigger a running workflow. |
- Add other nodes after the start node and connect each node together.
- Double click every node to edit the node content. If delete, right click the desired node and click Delete.
- Click Save button on the top to save the workflow.
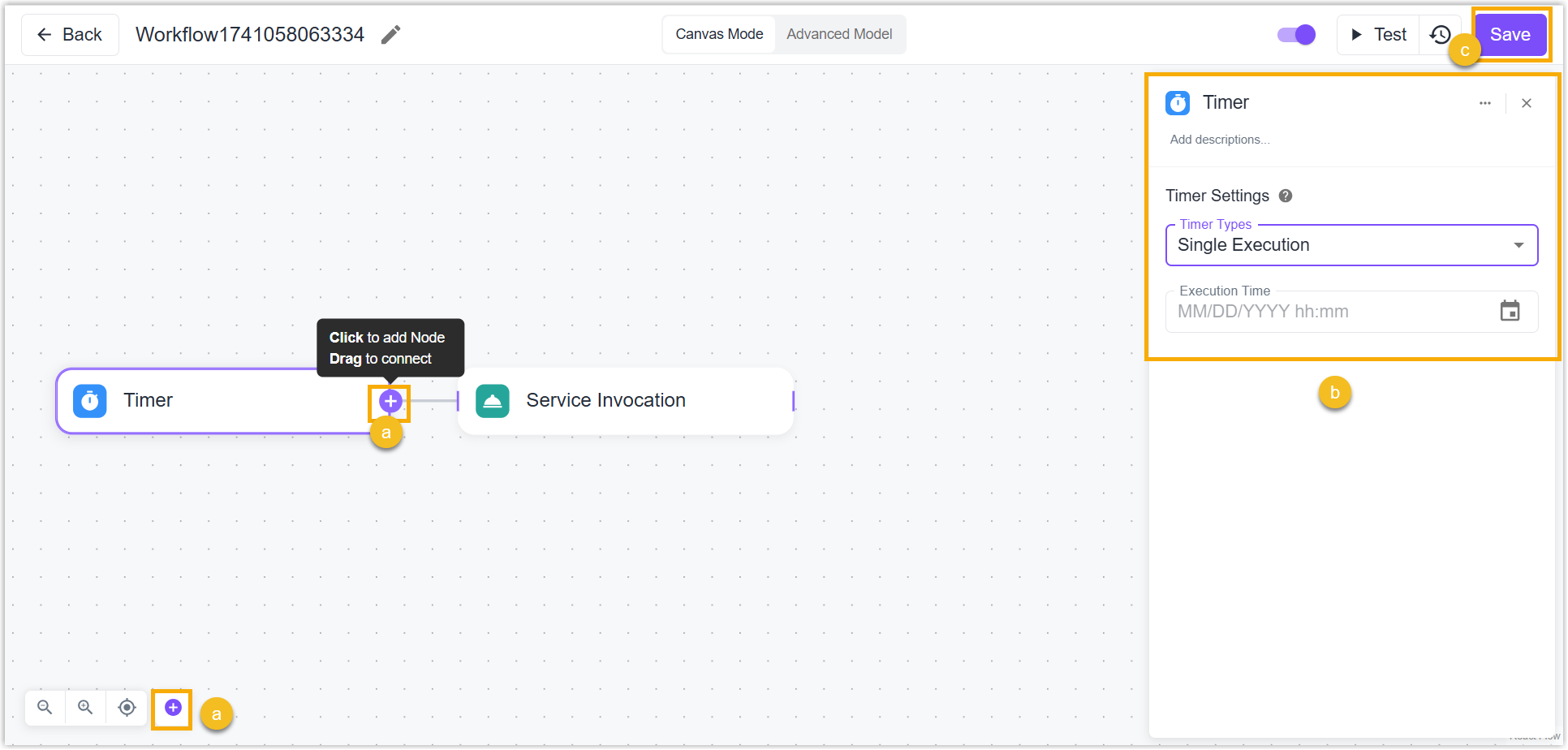
Test and Logs
Test
Workflow Test: Click Test to test if the nodes are valid or if the workflow can work well.
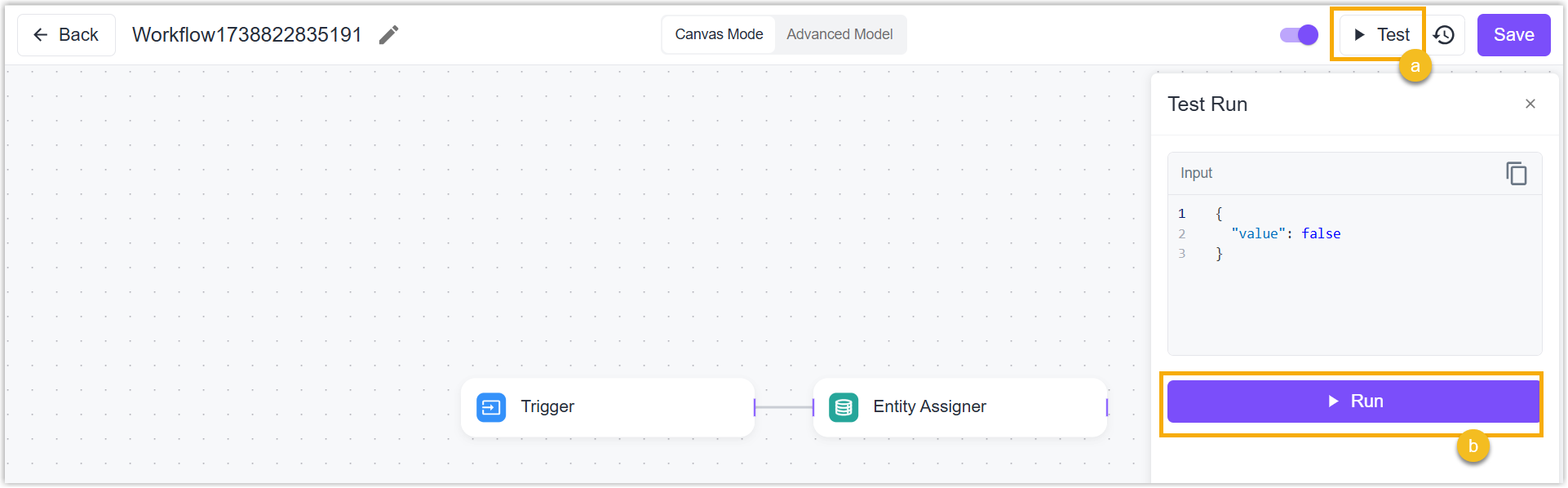
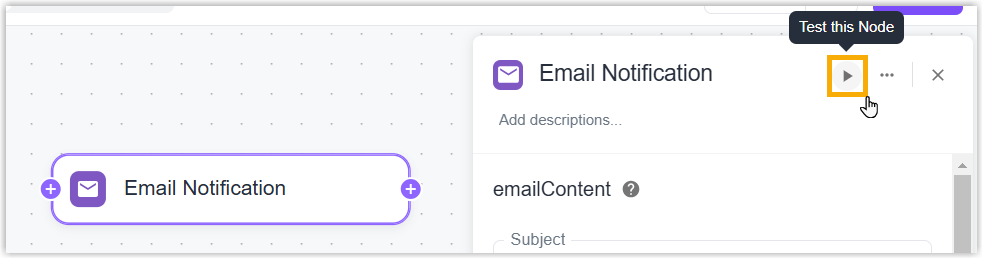
Node Test: Webhook, Code, and Email Notification Nodes support clicking Test the Node button to test whether the configuration works well.
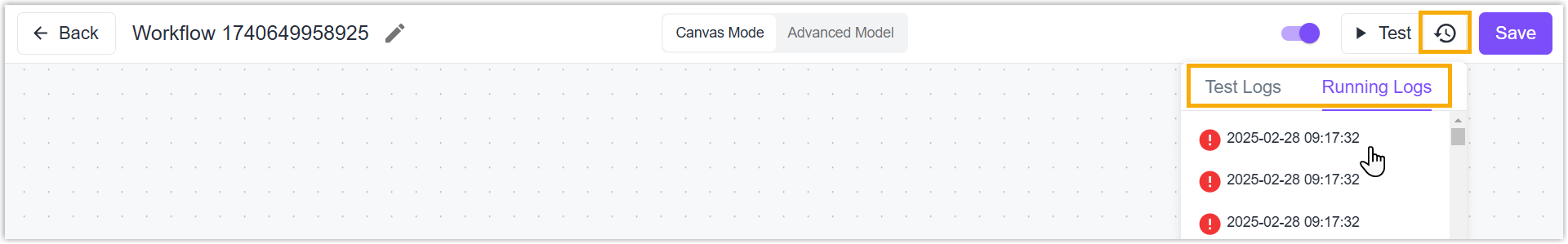
Logs
Running Logs: When a workflow is triggered every time, a running log will be generated to record the running status, inputs, outputs, and other information.
Test Logs: When clicking Test to test the workflow, a test log will be generated to record the running status, inputs, outputs, and other information.
Export and Import Workflow
Export: Select the desired workflow, click Export to export the workflow as JSON format file.
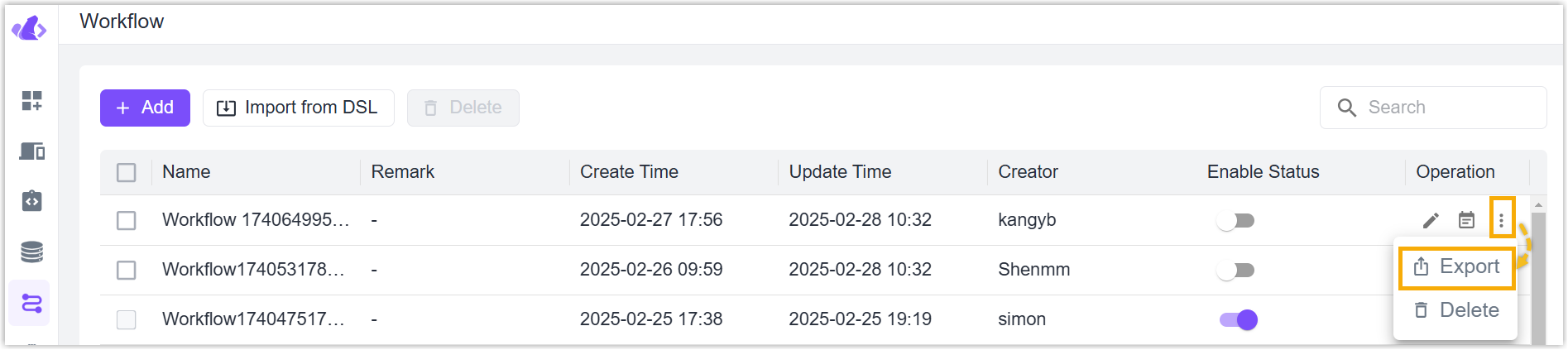
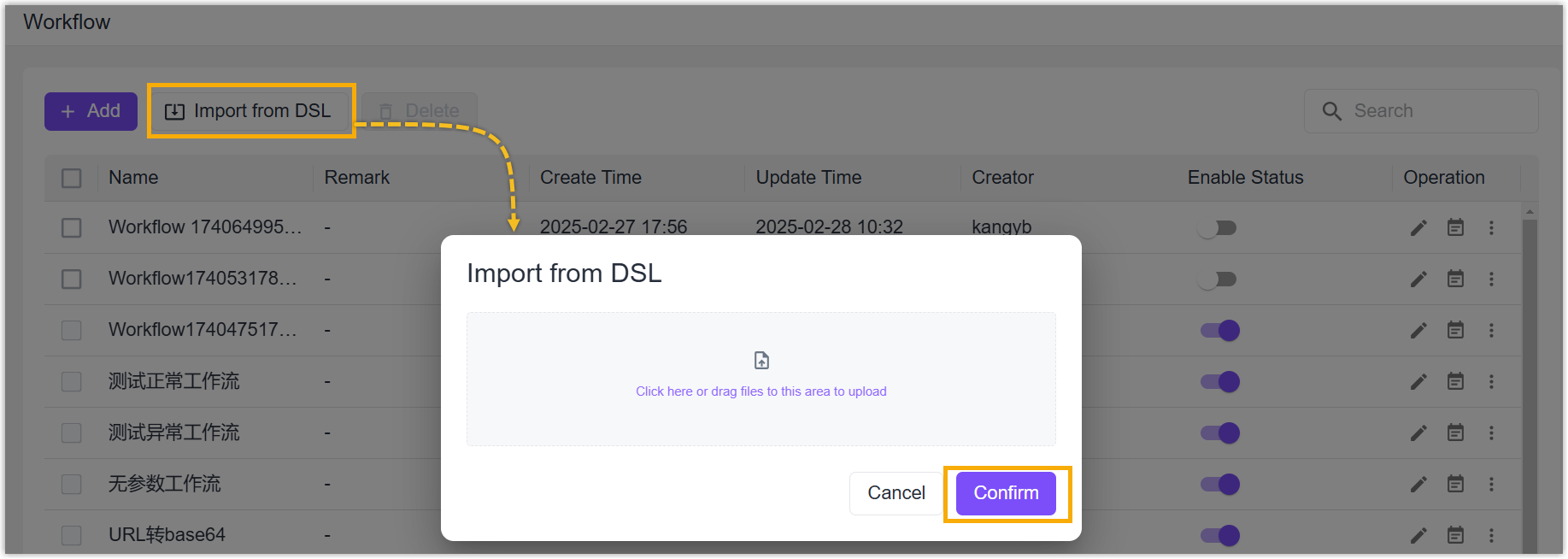
Import: Click Import from DSL to upload JSON format workflow files, click Confirm to save the settings.
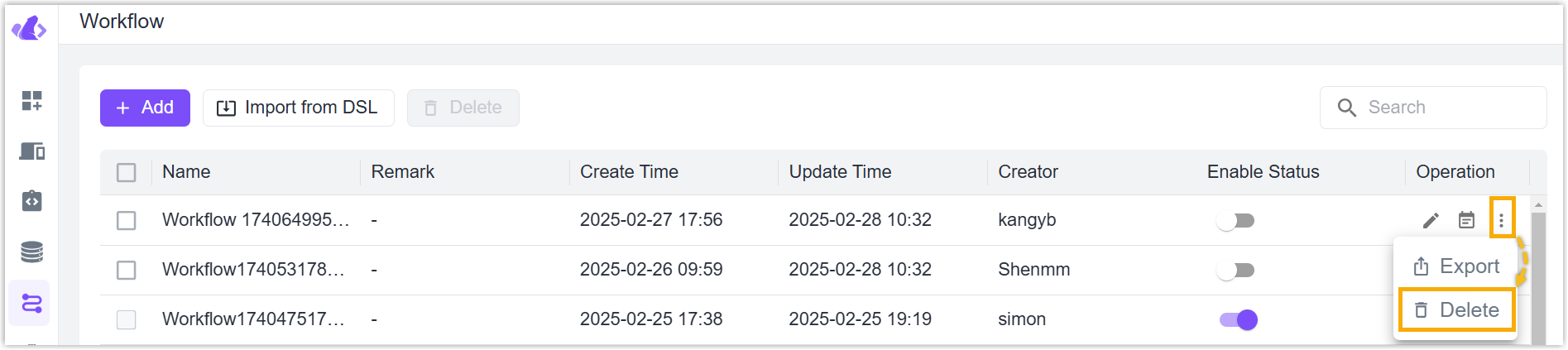
Delete Workflow
Delete one workflow: Click Delete icon of desired workflow to delete this workflow.
Delete workflows in bulk: check the boxes of desired workflows, click Delete button on the top to delete these workflows.
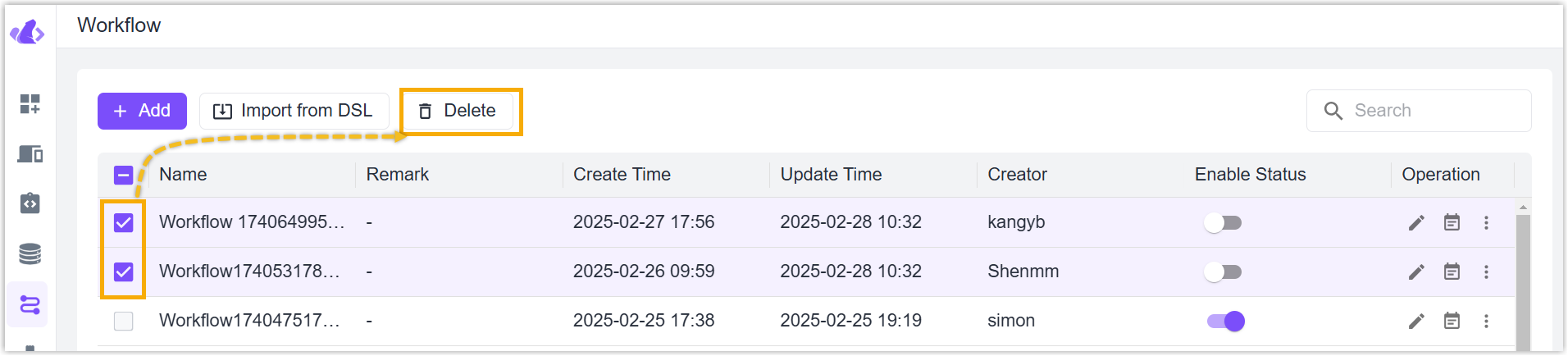
- The enabled workflows are not allowed to delete.
Node Introduction
Node is the basic unit of workflow. Beaver IoT supports the following nodes in series to build workflows for flexible applications.
Starting Node:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Timer | Trigger the workflow based on the schedule time or cycle. Example: schedule switch. |
| Trigger | Trigger the workflow by the Trigger widget on the Dashboards. Example: button switch. |
| Entity Listener | Trigger the workflow when any entity data changes. Example: threshold alarm. |
| MQTT Listener | Work as MQTT broker to listen for incoming MQTT messages to trigger a running workflow. |
| HTTP Listener | Work as HTTP server to listen for incoming MQTT messages to trigger a running workflow. |
External Node:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Email Notification | Send email notifications to recipients based on SMTP protocol, the subject and content of Email notifications can be customized. Besides, the Email contents support inserting variables of this workflow. Before sending emails, it is necessary to configure the SMTP client settings. |
| Webhook Push | Push the payload values to pre-configured Webhook URL address. If the payload is blank, the workflow will push all output contents from before nodes to the Webhook URL address. |
| HTTP Request | Call the external HTTP API. |
| Output | Output the variables of the workflow. This node is available when the start node is Trigger. |
If the SecretKey is typed in Webhook Push node, the header of the request will include below fields for legality verification:
SignatureTimestampNonce
Verification method:
- Step 1:
Payload=Timestamp + Nonce + Request Body - Step 2: Calculate the result of the
PayloadusingSecretKeyand Hmac256 algorithm,then convert the result to Hex format strings. - Step 3: Check if the calculation result is the same as
Signature. If yes, the request is judged as legal.
Action Node:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Entity Assigner | Assign the output values from preceding nodes to selected entities. |
| Entity Selection | Select the entities to pass into this workflow to work as the arguments of subsequent nodes. |
| Service Invocation | Invoke the services from entities or other workflows. |
| Code | Write code to achieve flexible data process functions. Beaver IoT supports these languages: JavaScript (ES6), Python(2.7), Groovy(4.0.26), and MVEL(2.5.2). Before writing, it is necessary to define the input arguments used in the codes; if you are required to pass the output results to subsequent nodes, it is also necessary to define the output variables. |
Control Node:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| IF/ELSE | When the logical condition is met (IF) or not met (ELSE), the subsequent nodes of this workflow are triggered to execute. One node supports the addition of 5 logical conditions at most, and one logical condition supports multiple sub-conditions and these sub-conditions can be connected by an AND or OR relationship. In addition, Beaver IoT supports writing the logical conditions by these languages: JavaScript (ES6), Python(2.7), Groovy(4.0.26), and MVEL(2.5.2). |